Amazigh culture Morocco is one of the oldest living cultural identities in North Africa, shaping traditions, language and daily life for thousands of years.

The Amazigh culture is one of the fundamental pillars of Moroccan identity. Present in North Africa for thousands of years, it has deeply shaped Morocco’s history, traditions, and way of life. Today, Amazigh heritage remains alive through language, rituals, craftsmanship, and artistic expressions that continue to enrich Moroccan culture.
Amazigh Culture Morocco: Origins and Traditions
The Amazigh people, also known as Berbers, are the indigenous inhabitants of North Africa. Their presence in Morocco dates back to ancient times, long before the arrival of the Phoenicians, Romans, or Arabs. Over centuries, the Amazigh civilization developed a strong social organization, belief systems, and ancestral knowledge closely connected to the Moroccan landscape.
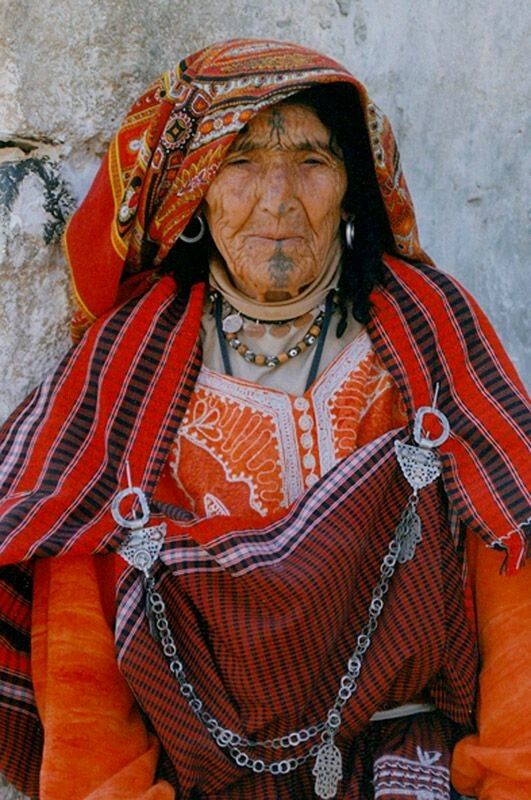

Despite external influences, Amazigh communities have preserved their identity while actively contributing to the formation of Moroccan culture as a whole.
Today, Amazigh culture Morocco remains a living heritage, influencing music, crafts, festivals and regional identities across the country.
The Amazigh Language: A Symbol of Identity
The Amazigh language, known as Tamazight, is a central element of Amazigh identity. It exists in several regional varieties, including Tarifit in the Rif region, Central Tamazight in the Middle Atlas, and Tachelhit in southern Morocco.

Since its recognition as an official language of Morocco, Tamazight has gained increasing visibility in education, media, and cultural life, helping to preserve and promote this ancestral heritage.
Amazigh Traditions and Rituals
Amazigh culture is expressed through numerous traditions passed down from generation to generation. Agricultural festivals, family ceremonies, and community rituals play a key role in social life within Amazigh regions.

One of the most important celebrations is Yennayer, the Amazigh New Year. This event marks a strong attachment to ancestral traditions and symbolizes renewal, prosperity, and harmony with nature.
Among the most significant traditions are:
- seasonal and agricultural celebrations,
- Amazigh wedding rituals rich in symbolism,
- collective songs and dances accompanying major life events.
These practices strengthen social bonds and preserve values of solidarity and respect for ancestors.
Amazigh Handicrafts: Ancestral Know-How
Amazigh craftsmanship holds a central place in Morocco’s cultural heritage. It is characterized by the use of geometric patterns and symbolic motifs transmitted over centuries.
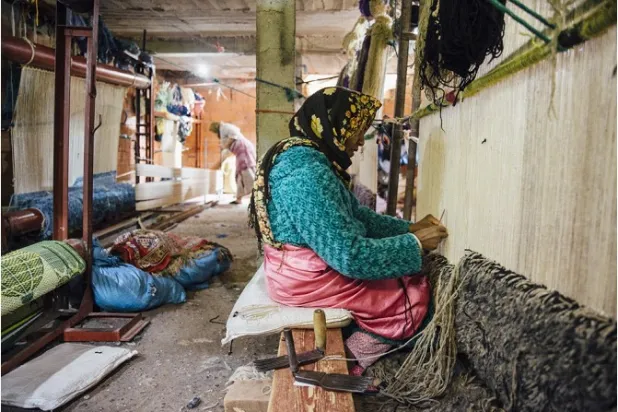

Silver jewelry, handwoven carpets, pottery, and traditional embroidery reflect unique expertise, where each shape and color carries cultural or spiritual meaning. These creations represent both artistic expression and cultural transmission.
Amazigh Architecture and Symbols
Traditional Amazigh architecture, especially kasbahs and collective granaries, demonstrates a strong adaptation to the environment. Built with earth, stone, and wood, these structures reflect a harmonious relationship between people and nature.
Amazigh symbols, widely present in architecture and decorative arts, often represent protection, fertility, and continuity of life.
Amazigh Culture in Contemporary Morocco

Today, Amazigh culture plays an increasingly visible role in Moroccan cultural life. Amazigh music, literature, cinema, and festivals contribute to its national and international recognition.
This dynamic helps preserve the authenticity of Amazigh heritage while integrating it into modern Moroccan society.
Conclusion
Amazigh culture is a living heritage deeply rooted in Morocco’s history. It is one of the essential foundations of national identity and a key component of the country’s cultural richness and diversity.
Understanding Amazigh culture means understanding the soul of Morocco—a country shaped by the coexistence of civilizations and oriented toward the future.
FAQ – Amazigh Culture in Morocco
❓ What is Amazigh culture in Morocco?
Amazigh culture in Morocco refers to the traditions, language, customs and heritage of the indigenous Amazigh people, one of the oldest populations in North Africa. It plays a central role in Moroccan identity.
❓ Who are the Amazigh people?
The Amazigh (also known as Berbers) are the native inhabitants of North Africa. In Morocco, they have preserved their language, traditions and cultural practices for thousands of years.
❓ What language do the Amazigh people speak?
Amazigh people speak Tamazight, which is an official language of Morocco alongside Arabic. It includes several regional varieties such as Tarifit, Tashelhit and Central Atlas Tamazight.
❓ What are the main Amazigh traditions?
Amazigh traditions include music, dance, oral poetry, traditional clothing, festivals such as Yennayer (Amazigh New Year), and symbolic art often expressed through tattoos, jewelry and architecture.
❓ Why is Amazigh culture important in Morocco today?
Amazigh culture remains a living heritage in Morocco, influencing music, crafts, cuisine and social life. Its recognition strengthens cultural diversity and preserves Morocco’s historical roots.
shaped history, language and traditions, as explained by Encyclopædia Britannica in its overview of the Amazigh (Berber) people

